
Blisters are pockets of fluid that occur under the top layer of your skin. These fluid pockets are usually filled with pus, blood, or serum. Blisters may itch or hurt and can appear as a single bubble or in clusters.
The most common types of blisters are friction blisters. This type of blister may be caused by wearing shoes that are too tight. Friction blisters can also occur on the hands. A change in temperature may also cause blisters on the feet. In the freezing air, frostbite on your toes can lead to blisters, as well as sunburn from hot weather.
The best way to treat a blister is to keep it clean and dry. Most blisters will get better on their own. Once the skin absorbs the fluid within the blister, it will flatten and eventually peel off. You should avoid popping your blister unless you podiatrist does it for you. Additional treatment options include applying an ice pack to the blister or using over-the-counter blister bandages to cover the affected area.
If your blister becomes discolored, inflamed, or worsens it is advised that you speak to your podiatrist. Blisters that are yellow, green, or purple may be infected and require immediate medical attention. Blisters that are abnormally colored may be a sign of a more serious underlying health condition such as herpes.
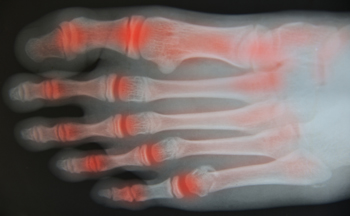
Rheumatoid arthritis, or RA, is an auto-immune disease that causes pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints. The feet, which contain multiple joints, are often affected by this inflammatory condition. The immune system, instead of protecting the joints, sends antibodies into the lining of the joints causing the tissue surrounding the joint to become inflamed. This results in damage to the bones, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. Many people are affected by RA, but most develop it between the ages of 40 and 50. Women are three times more likely to have rheumatoid arthritis than men, largely due to hormonal differences. Also, it affects many people who smoke or have a genetic tendency toward the disease. RA causes throbbing and aching pain, and may induce fatigue and fever along with a loss of appetite. Rheumatoid arthritis is not curable, but measures may be taken to reduce the symptoms. If you think you may have RA that is affecting your feet, it is suggested that you consult a podiatrist for treatment options.
Because RA affects more than just your joints, including the joints in your feet and ankles, it is important to seek early diagnosis from your podiatrist if you feel like the pain in your feet might be caused by RA. For more information, contact one of our podiatrists of Jill Einhorn, DPM and James Einhorn, DPM. Our doctors will assist you with all of your podiatric concerns.
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s own immune system attacks the membranes surrounding the joints. Inflammation of the lining and eventually the destruction of the joint’s cartilage and bone occur, causing severe pain and immobility.
Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Feet
Although RA usually attacks multiple bones and joints throughout the entire body, almost 90 percent of cases result in pain in the foot or ankle area.
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Quick diagnosis of RA in the feet is important so that the podiatrist can treat the area effectively. Your doctor will ask you about your medical history, occupation, and lifestyle to determine the origin of the condition. Rheumatoid Factor tests help to determine if someone is affected by the disease.
If you have any questions please feel free to contact our offices located in Brooklyn and Astoria, NY . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot and ankle needs.
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a chronic progressive disease that attacks several joints throughout the body. It is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joints. As a result, the tissue inside the joints, called synovium, starts to thicken and causes pain around the joints. The synovium is responsible for creating a fluid that lubricates the joints to help them move. Approximately 1.5 million people in the United States have Rheumatoid Arthritis. Women are almost three times as likely to have RA compared to men, and it’s disease usually begins between the ages of 30 and 60. People who have a genetic history of RA are more likely to develop the disease.
Symptoms of RA may include the following sensations in the joints: pain, tenderness, swelling, redness, warmth, stiffness, and loss of range. Swollen joints are a very common symptom for those with the disease. At times, it may be minimal, but it may also be very apparent. Another typical symptom is joint stiffness. Doctors will often use the direction of morning stiffness to measure the severity of a patient’s joint inflammation. Other RA symptoms include limping, anemia, fever, and fatigue.
To diagnose RA, your podiatrist will typically request x-rays to see how much damage there is in the joints. Blood tests may also be performed to show if there are any signs of anemia, or antibodies such as the rheumatoid factor. If you have previously been diagnosed with RA, you should know the disease may spread to your feet and ankles.
There are many non-surgical options that can be used to treat this ailment. Some of these options include physical therapy, foot massages, orthotics, bracing, supportive shoes, and steroid injections. Physical therapy is useful because it will help stretch and strengthen the joints in both the foot and ankle to improve joint function. Massages can help improve blood circulation which will be good for the feet. Choosing proper footwear will allow you to walk with comfortability if you are a sufferer from RA. Lastly, bracing will help stabilize the foot joints, limit deformities and decrease pain.
In severe cases, surgery may be a treatment option that should be considered. For those who cannot walk without experiencing pain and those whose deformities can not be managed with braces, surgery should be considered. Your podiatrist will recommend surgery if he or she believes it will improve your foot biomechanics.

Pain in the joint of the big toe, termed hallux rigidus, is a form of osteoarthritis caused by the wearing away of cartilage between the base of the big toe and the first metatarsal bone of the foot. This condition often affects runners, as the big toe takes the brunt of the continual pounding with each step. Hallux rigidus often develops in runners between the ages of 30 and 60. Some possible causes include having flat feet or overpronation, which is when the foot rolls inward 15 percent or more with each step. Overtraining, a stubbed toe, gout, a toe deformity, or genetics may also play a role in the development of hallux rigidus. Limited mobility and stiffness in the big toe joint are early symptoms of this disorder. In addition, a runner may experience pain and swelling on top of the big toe. Changing to footwear with a larger toe box and stiffer sole can help relieve the pressure on the big toe. Certain medications may also help. A podiatrist can examine the toe, determine the cause of the joint pain, and offer appropriate treatment solutions. It is suggested that you make an appointment today.
Toe pain can disrupt your daily activities. If you have any concerns, contact one of our podiatrists of Jill Einhorn, DPM and James Einhorn, DPM. Our doctors can provide the care you need to keep you pain-free and on your feet.
What Causes Toe Pain?
Most severe toe pain is caused due to a sports injury, trauma from dropping something heavy on the toe, or bumping into something rigid. Other problems can develop over time for various reasons.
Toe pain can be caused by one or more ailments. The most common include:
When to See a Podiatrist
Diagnosis
In many cases the cause of toe pain is obvious, but in others, a podiatrist may want to use more advanced methods to determine the problem. These can range from simple visual inspections and sensation tests to X-rays and MRI scans. Prior medical history, family medical history, and any recent physical traumatic events will all be taken into consideration for a proper diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatments for toe pain and injuries vary and may include shoe inserts, padding, taping, medicines, injections, and in some cases, surgery. If you believe that you have broken a toe, please see a podiatrist as soon as possible.
If you have any questions please feel free to contact our offices located in Brooklyn and Astoria, NY . We offer the newest diagnostic tools and technology to treat your foot and ankle needs.
Toe pain can originate from corns, calluses, hammertoes, and bunions, as well as ingrown toenails, sprains, fractures, and dislocations. Corns develop as the toe rubs against the inside of a shoe which causes the skin to thicken as a form of protection. A corn is typically cone-shaped and has a small, hardened spot that points inward. When a corn is pressed into the skin, the toe becomes painful. Corns usually form on the top or side of the toe. A callus is also a thickened patch of skin that generally forms on the bottom of the foot. Calluses are the result of friction from the toe rubbing against the inside of a shoe. They may also occur by walking barefoot or having flat feet. A hammertoe is a bump on the knuckle of the second toe that is produced by wearing shoes that are too short for your feet. The bony protrusion rubs against the top of the shoe causing pain and irritation. A bunion is a malformation of the big toe. The base of the big toe pushes away from the smaller toes, forcing the top of the big toe to press toward the other toes. Bunions can be hereditary, or they can result from injury to the toe joint or from wearing high heels with a narrow toe box. The toe becomes inflamed, and a bump may develop at the end of the misplaced bone. Ingrown toenails typically affect the big toe and its surrounding skin. The nail will dig into the skin and become painful. Wearing tight or narrow shoes that compress the big toe causes the nail to grow into the fleshy part of the toe. Cutting toenails incorrectly can also add to the development of an ingrown toenail. A toe sprain originates from a torn or stretched ligament. Strapping the injured toe to the toe next to it for stabilization is common. A broken or fractured toe usually occurs from trauma like dropping a heavy object on it or bumping into something extremely hard and rigid. Osteoporosis, a thinning of the bones, can also bring about toe fractures.
Any of the conditions mentioned can lead to pain and irritation. While some are more serious than others, seeking an examination and diagnosis from a podiatrist is a good idea. A podiatrist can treat each ailment and get you back on your feet again without pain.
An ankle sprain occurs when one or more ankle ligament gets overly stretched. Ligaments are strong bands of tissue that bind and support the bones and other structures that make up the ankle. In more severe ankle sprains, the ligament(s) tear—either partially or completely—and there may be an audible popping noise at the moment of injury.
Ankle sprains are quite common and can occur when the ankle rolls outwardly (eversion) or inwardly (inversion), causing the ligament(s) to stretch beyond normal limits, or even tear. Falls, twists, or blows to the ankle during sports or other activities can cause this injury, as well as wearing improper footwear, running on uneven surfaces, or having weak ankles.
Depending on the injury’s severity, an ankle sprain will be classified as Grade I, Grade II, or Grade III. Grade I sprains involve ligament(s) being overly stretched but not torn, with symptoms of mild pain, swelling, and ankle instability. There may also be some difficulty bearing weight. A Grade II sprain usually involves a partial tear of the ligament which brings more intensity in these symptoms, along with possible bruising. With a Grade III sprain, the ligament is completely torn, the symptoms are severe, and it may not be possible to put weight on the affected foot at all.
To diagnose and grade an ankle sprain, a podiatrist will perform a physical examination, checking for tenderness and range of motion in the ankle. For more severe sprains, X-rays or other imaging studies may be necessary.
It is vitally important to have an ankle sprain treated properly as improper healing often leads to future ankle sprains and possibly even chronic ankle stability. Treatment for an ankle sprain will vary, depending on its severity, and may include the RICE method (Rest/Ice/Compression/Elevation), physical therapy, bracing, medications, and possibly even surgery to repair a torn ligament. Rehabilitation is very important for the sprain to heal properly and to restore functionality.

A hard lump on the side of the toe may be a bunion. It is considered to be a deformity, and large bunions may cause difficulty while wearing shoes. Women can be prone to developing bunions as a result of the high heels that are worn. They generally provide little room for the toes to move freely in, and this may cause the side of the big toe to rub on the shoe. Some patients notice their toes shifting toward each other, as the bunion may cause this misalignment. Corns and calluses may develop on top of the bunion, and putting a protective pad over it may bring relief. Pain may be caused by a bunion, and the toe may become numb or have a burning sensation. If you have developed a bunion, it is suggested that you speak to a podiatrist, who can offer you relief solutions, which may include minor surgery for removal.
If you are suffering from bunions, contact one of our podiatrists of Jill Einhorn, DPM and James Einhorn, DPM. Our doctors can provide the care you need to keep you pain-free and on your feet.
What Is a Bunion?
A bunion is formed of swollen tissue or an enlargement of boney growth, usually located at the base joint of the toe that connects to the foot. The swelling occurs due to the bones in the big toe shifting inward, which impacts the other toes of the foot. This causes the area around the base of the big toe to become inflamed and painful.
Why Do Bunions Form?
Genetics – Susceptibility to bunions are often hereditary
Stress on the feet – Poorly fitted and uncomfortable footwear that places stress on feet, such as heels, can worsen existing bunions
How Are Bunions Diagnosed?
Doctors often perform two tests – blood tests and x-rays – when trying to diagnose bunions, especially in the early stages of development. Blood tests help determine if the foot pain is being caused by something else, such as arthritis, while x-rays provide a clear picture of your bone structure to your doctor.
How Are Bunions Treated?
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our offices located in Brooklyn and Astoria, NY . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
Bunions are large bony bumps at the base of the big toe. Medically known as hallux valgus, a bunion is a misalignment of the metatarsophalangeal joint, or big toe joint. The misalignment will generally worsen with time if left untreated.
The exact cause of bunions is unknown, with genetics seen as a potential cause. High heels and poorly-fitted footwear, rheumatoid arthritis, and heredity all seem to be potential factors behind the exacerbation of bunions. Women have been found to be more likely to develop bunions in comparison to men.
Bunions do not always produce symptoms. The best way to tell is if the big toe is pushing up against the next toe and there is a large protrusion at the base of the big toe. You may or may not feel pain. Redness, swelling, and restricted movement of the big toe may be present as well.
Podiatrists use a variety of methods to diagnose bunions. If there are symptoms present, podiatrists will first consider that it is a bunion. If not, a physical examination will be conducted to check function of the big toe. Finally, an X-ray may be taken to view the extent of the bunion and confirm it is a bunion.
Typically, nonsurgical methods are used to treat bunions, unless the bunion has become too misaligned. Orthotics, icing and resting the foot, roomier and better fitted shoes, taping the foot, and pain medication are usually utilized first. If the bunion doesn’t go away or causes extreme pain, surgery may be required. Surgeons will either remove part of the swollen tissue or bone to straighten the toe out.
If you have a bunion, it is recommended to see a podiatrist. The longer it is left untreated, the worse it may get. Podiatrists can properly diagnose and treat a bunion before it gets worse.